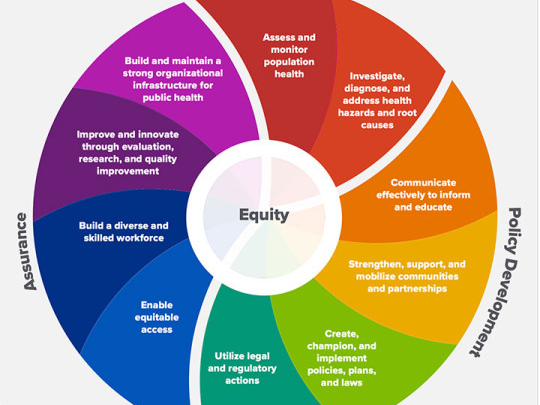
Public Health Management encompasses a variety of functions aimed at improving and protecting the health of populations. Here are some key functions:
- Disease Prevention and Control-: Public health management focuses on preventing the spread of diseases by implementing vaccination programs, promoting hygiene, and organizing campaigns to prevent communicable and non-communicable diseases.
- Health Education and Promotion-: It involves educating the public about health risks, healthy lifestyles, and disease prevention. This includes promoting healthy behaviors like proper nutrition, physical activity, and avoiding harmful substances.
- Health Policy Development-: Public health managers are involved in shaping health policies that govern healthcare delivery, public health initiatives, and resource allocation to ensure the overall well-being of communities.
- Surveillance and Monitoring-: Tracking health trends, monitoring outbreaks, and analyzing data to identify public health threats are critical. Public health management uses surveillance systems to track the spread of diseases and evaluate intervention effectiveness.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response-: In times of health emergencies, like pandemics or natural disasters, public health managers coordinate responses, ensuring that resources, personnel, and communication strategies are in place to mitigate impacts.
- Health Program Implementation-: Managers oversee and implement public health programs designed to address specific health issues, such as maternal and child health programs, immunization campaigns, and nutrition interventions.
- Resource Allocation and Budgeting-: Efficient allocation of financial and human resources is crucial. Public health management ensures that funds and personnel are distributed appropriately to maximize health outcomes across various projects and programs.
- Collaboration and Partnerships-: Public health management works with governmental agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and international bodies to address global health issues, share data, and improve healthcare infrastructure.
- Equity in Healthcare Access-: A central function is ensuring that healthcare services are accessible to all population groups, particularly marginalized and vulnerable communities. This includes addressing social determinants of health like housing, education, and income inequality.
- Regulation and Enforcement-: Ensuring that public health laws, regulations, and standards, such as food safety, workplace health, and environmental regulations, are enforced to protect the public from health hazards.
Each of these functions plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving public health, contributing to a healthier society.
